News
An innovator in developing therapeutic antibodies, fusion proteins and circRNA
At the 2026 J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference, T-cell engagers (TCEs) emerged as a central theme across industry presentations. Leading multinational pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech firms consistently positioned TCEs as a scalable platform with significant commercial and therapeutic potential. Two industry consensus emerged across the presentations: First, next-generation engineering approaches, including masked/prodrug activation, low-affinity or fast-off-rate CD3 binding, and tumor microenvironment-responsive mechanisms, are being applied to enhance safety profiles and expand therapeutic windows. Second, the clinical pipelines are rapidly expanding beyond hematologic malignancies into solid tumors and autoimmune/inflammatory indications. As the field enters a pivotal phase of accelerated clinical validation and commercial scale-up, capital allocation and R&D investment are increasingly concentrated on TCE development. The technology has advanced beyond proof-of-concept exploration into rapid engineering optimization and large-scale clinical readouts. TCEs now represent one of the most promising and widely endorsed next-generation modalities in the bispecific and multispecific antibody space.
The core of TCE technology lies in T-cell activation. Meanwhile, two other technologies, in vivo TCE and in vivo CAR-T, are generating significant interest recently. These three therapies have their own advantages and disadvantages. Here, we are going to deep dive into the key differences among them and explain the potential of CD3-VHH in optimizing T-cell immunotherapies.
What are TCEs, in-vivo TCEs and in-vivo CAR-Ts ?
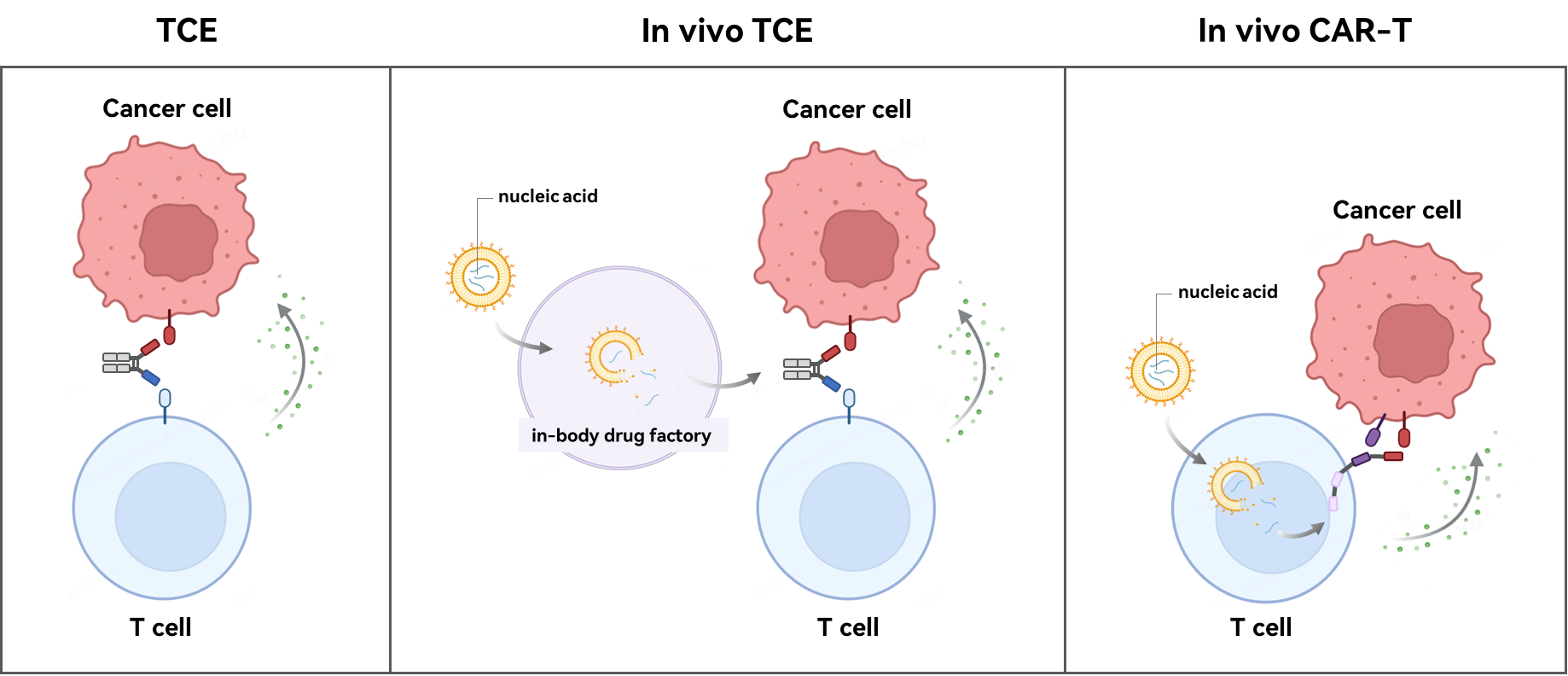
• TCEs are bispecific antibodies, acting as a bridge to simultaneously bind tumor/pathogenic immune cells and T cells, enabling T cells to mount a precise attack. The production of TCEs does not require modification of the patient’s immune cells. BLINCYTO and TECVAYLI for hematologic malignancies are examples of TCE immunotherapies.
• In vivo TCEs, acting as an “in-body drug factory,” deliver nucleic acids encoding TCEs into cells via vectors such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) or adeno-associated viruses (AAVs). There, TCEs are expressed and functionalized intracellularly. This avoids complex production and purification processes, and can reduce systemic toxicity and dosing frequency by optimizing the vector design.
• In vivo CAR-Ts, acting as an “in-body T-cell engineering factory,” deliver nucleic acids encoding CARs into T cells, transforming them in situ into CAR-T cells with specific cytotoxic capabilities. It does not require ex vivo isolation, culture, and modification of T cells; compared with traditional CAR-T, the process is simpler, faster, and more affordable.
How are CD3-VHHs optimized for Better T-Cell Immunotherapies
Current T-cell immunotherapies have their own strengths and weaknesses. The drug formats suited to different diseases vary significantly. There remains substantial room for optimization. A CD3-VHH with a molecular weight only 1/10 that of conventional antibodies is becoming valuable in upgrading T-cell immunotherapies due to their unique advantages.
1. CD3-VHH for TCEs: Strong Penetration, Low Toxicity, Flexible Design
a. Their small molecular size can easily penetrate solid tumors, which traditional TCEs find difficult to enter, thereby increasing intratumoral drug concentration.
b. VHHs are small molecules and, after humanization, have extremely low immunogenicity, reducing anti-drug antibody positivity.
c. Their small size and modular nature streamline the design of multispecific engagers, facilitating both flexible positioning and half-life extension.
d. They enable precise regulation of T-cell activation strength, reducing cytokine release and lowering the risk of severe adverse reactions.
2. CD3-VHH for In Vivo TCEs: Easy to Load, High Expression, Strong Stability
a. The encoding gene is only 400 bp (traditional antibody is 1.5 kb), making it highly compatible with AAVs, LNPs and other vehicles, and capable of carrying multiple target sequences simultaneously.
b. The nature of being small promotes efficient protein folding, resulting in significantly higher in vivo TCE expression levels compared to traditional systems.
c. They are heat-resistant and protease-resistant, with a half-life that can be easily regulated to reduce immune responses caused by in vivo degradation.
3. CD3-VHH for In Vivo Targeted Delivery: Strong Penetration, Easy Engineering, High Safety
a. They can penetrate dense tissues, such as vascular endothelium and tumor microenvironment, and enrich in T cells, addressing the core challenges of traditional CD3 antibodies — poor penetration and weak targeting.
b. VHHs can be easily constructed into conjugates or used to modify vectors, and their valency can be designed on demand to adjust targeting strength, fitting all in vivo delivery modes.
c. Lacking an Fc region avoids nonspecific ADCC/CDC effects; their half-life can be easily regulated to accommodate repeated dosing for chronic diseases.
CD3-VHH Developed by Fapon Biopharma
Fapon Biopharma has identified and developed a CD3-VHH with excellent human-monkey cross-reactivity — demonstrating robust functional activity and developability, providing a superior solution for the development of related therapies. A series of affinity-directed modifications were subsequently conducted on the CD3-VHHs, yielding variants with a range of affinities. Most variants preserved high human-monkey cross-reactivity during the modification process. These CD3-VHH sequences with varying affinities offer more possibilities for treating different diseases in the future.
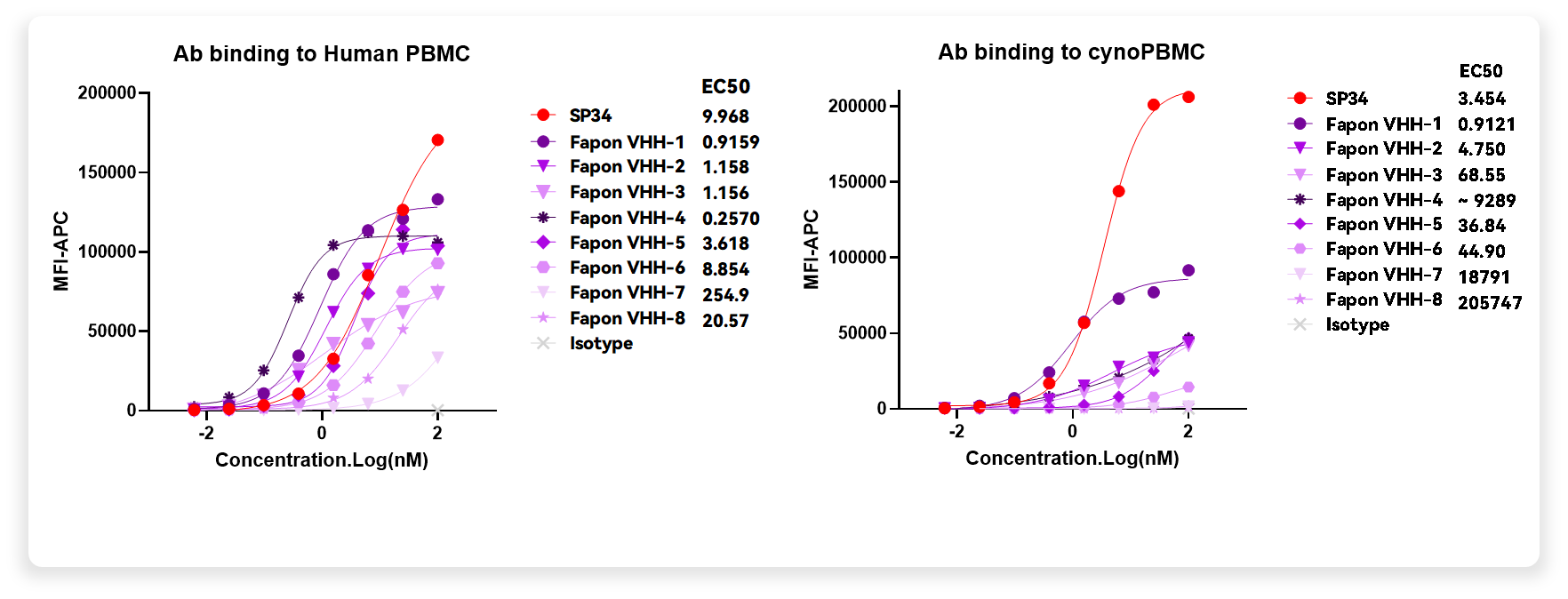
In addition to CD3-VHH, Fapon Biopharma also developed VHHs with excellent human-monkey cross-reactivity targeting CD7, CD8, CD19, and BCMA, which can be used in TCE, in vivo TCE, and in vivo CAR-T for product development.
Learn more about Fapon Biopharma's CD3-VHHs and would like to collaborate, please visit us at the AACR Annual Meeting 2026 at booth #3856, or contact us via the email below!
Asia-Pacific: BDAP@fapon.com
USA, Europe and other regions: biopharmaBD@fapon.com
About Fapon Biopharma:
Fapon Biopharma specializes in discovering and developing biologics for cancer treatment, autoimmune diseases and other diseases where there are unmet medical needs. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies, we have built advanced drug discovery platforms, including an antibody discovery platform based on the globally leading mammalian cell display technology, a platform for generating IL-10M fusion proteins, a TCE platform based on cross-species CD3-VHH of human and monkey. With a differentiated pipeline of leading drug candidates, we have established capabilities that cover the entire drug development process from drug discovery, preclinical research, Chemistry, Manufacturing and Controls (CMC) to early clinical development. Committed to innovation, we strive to deliver safer, more efficacious, affordable, and accessible biologics for everyone.

+86 769 86088555, Ext. 0

biopharma@fapon.com

3F–4F, Building 10, Dongguan–Taiwan Bio-Tech Collaborative Incubation Center, 1 Taoyuan Road, Dongguan, Guangdong Province, China

Scan and follow Fapon LinkedIn Page
© Guangdong Fapon Biopharma Inc. All rights reserved.
Guangdong ICP No. 2024177910-1Links: